How to calculate inventory turnover ratio
What is inventory turnover?
Different products sell at different rates. Some will fly out of the door as soon as you get stock, while others that are slow-moving will sit on the shelves until you have to give them away or write them off. Most of your stock will be somewhere in the middle. You can track this using inventory turnover – the time it takes from bringing an item into stock to selling it.
Inventory turnover (also known as stock turnover) measures how well a business manages its inventory to meet demand. It can help improve decision-making regarding pricing, manufacturing, marketing and purchasing.
Low inventory turns can indicate poor sales or excess inventory. Higher inventory turns can highlight strong sales and good inventory stocking policies. However, inventory turnover will likely fluctuate depending on changes in demand, supply chain disruption and other market factors.
What is the inventory turnover ratio?
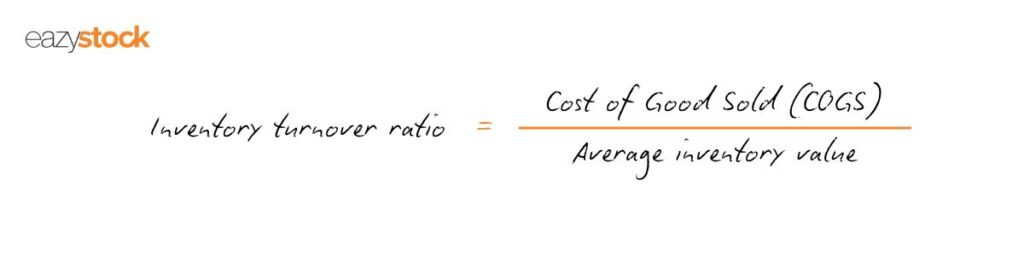
Inventory turnover ratio (also known as stock turnover ratio) is an accounting and inventory management KPI used to measure how often stock is sold (used or replaced) within a fixed period, relative to its costs of goods sold (COGS). You can use the formula to calculate how many days it will take to sell the inventory you hold.
It is often used to measure the efficiency of warehouse or stock control processes to meet demand. The inventory turnover ratio is the ratio of the cost of goods sold to the average stock held.
How do I calculate inventory turnover ratio?
To calculate the inventory turnover ratio, take the total cost of goods sold (COGS) over a specific period and divide it by the average inventory value during the same period.
To calculate the average inventory value, add your opening inventory value to your closing inventory value and divide it by 2.

Let’s look at an example of a company in the building materials industry. The ABC Doors and Windows Company wanted to calculate its inventory turnover for the last 12 months.
- The cost of goods sold over this period was £815,000
- The opening stock value was £140,000
- At the end of this period, the stock was valued at £163,000.
Using the inventory turnover calculation, we get 5.4 inventory turns per annum:

To calculate the average number of days it takes to turn the stock, we divide 365 days (12 months) by the 5.4 inventory turns, resulting in 68 days:

The importance of having a good inventory turnover ratio
Most stock-holding businesses will have significant money tied up in inventory. It’s, therefore, essential to keep selling these items and converting the investment back into accessible cash. Using an inventory turnover ratio helps businesses better understand how efficient they are at doing this.
A high stock turnover ratio generally indicates that a business is managing its inventory effectively. The company isn’t overbuying stock or wasting money on warehousing space. Instead, it’s meeting demand by selling what it buys and bringing cash back into the business to cover the cost of goods sold.
In contrast, companies with a low inventory turnover ratio are often more inefficient in replenishment activities leading to excess inventory, which becomes unsold. They will be overstocking slow-moving inventory and escalating carrying costs (holding costs), e.g. warehouse costs, insurance, utilities etc. Cash will be tied up in inventory for longer and there’s a higher risk of items becoming obsolete and dead stock, which will eat into profit margins as the stock fails to sell.
In summary, healthy stock turnover can improve profitability because:
- Items that turn faster have lower carrying costs, which positively impacts the bottom line
- Cash is constantly freed-up for reinvestment
- Businesses can remain responsive to the marketplace and react to changes in demand
- There’s less chance of excess stock becoming obsolete and being sold at a loss.
What is a good inventory turnover ratio?
When analysing your stock turnover ratio, remember it will be relative to the stock you sell and your industry. For example, an ideal stock turnover ratio for a fast-moving consumer goods retailer will be much higher than for a company that sells high-end furniture.
Usually, businesses with low gross margins need to turn their inventory more often, so they can offset their low per-unit profit with higher sales volumes.
Ideally, you’d look to benchmark your turnover against similar businesses in your industry, but if this proves challenging, look at your trends and how to improve them.
However, there’s a fine line between having a high stock turnover ratio and running out of stock. Insufficient inventory levels can lead to lost sales opportunities, unhappy customers and a damaged reputation over time.
So how do you optimise your inventory turnover rates?
Optimising inventory turnover
If you search the internet, you’ll find many blog posts and articles telling you that to improve inventory turnover you need to reduce your order quantities, e.g. order less, more often. How do you do this without risking stockouts? Do you have the inventory replenishment planning infrastructure and supplier flexibility?
The key is to stock the right amounts of the right type of products at the right time. This is because every item in your warehouse is different – they will have various sales costs and demand patterns, and the time of year, market trends and promotions will affect them differently.
Read more about these factors and improve your inventory turnover here.
If you’d like to find out how EazyStock inventory optimisation software can improve your stock turn ratio, without affecting your stock availability, contact us on 0121 312 2992 or request a demo.